The History of Twitter: Key Milestones and Major Changes

From Jack Dorsey’s first tweet in 2006 to Elon Musk’s high-profile $44 billion acquisition in 2022, Twitter has reshaped how people communicate online. Here’s a complete look at Twitter’s history, timeline, and product evolution.
Twitter Timeline Summary
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2006 | Jack Dorsey posts first tweet |
| 2009 | Verified accounts, retweets, and hashtags launched |
| 2013 | Twitter files for IPO |
| 2015 | Live streaming via Periscope |
| 2017 | Twitter becomes profitable |
| 2021 | Jack Dorsey resigns; Spaces launched |
| 2022 | Elon Musk announces $44B acquisition |
The First Tweet in History
The first tweet was posted by Twitter co-founder Jack Dorsey on March 21, 2006: “just setting up my twttr.”
How Did Twitter Start?
Twitter began as Twttr, a side project inside podcasting company Odeo. The platform followed a naming trend of dropping vowels, but soon rebranded to “Twitter.” It officially launched to the public in July 2006.
Key Twitter Milestones Over the Years
2006: The Birth of Twitter
Twitter was conceptualized in March 2006, and its first tweet was posted that month. The public product went live in July and slowly started gaining traction.
2009–2010: Verified Accounts and Retweets Arrive
Twitter added essential features to shape its core experience. Verified accounts, hashtags, and retweets helped users follow trends and amplify content.
- June 2009: Verified accounts launched.
- July 2009: Hashtags became clickable.
- Nov 2009: Retweet button introduced.
- Sept 2010: New media-rich interface (“New Twitter”) launched.
2011–2012: Redesign and iOS Integration
Apple’s iOS integration and a redesigned website helped Twitter scale faster and support brands with visual profiles and embedded media.
- Oct 2011: Twitter integrated into iPhone/iOS.
- Dec 2011: Website redesign focused on ease of use and branding.
- 2012: Tweet links began showing content previews.
2013–2014: IPO and Multimedia Push
Twitter filed for IPO and introduced more media formats. Vine and GIF support were aimed at making the platform more visual and engaging.
- Jan 2013: Launched Vine for looping videos.
- Sept 2013: Filed for IPO; raised $1.8B in November.
- June 2014: GIFs supported across all platforms.
2015–2016: Live Video and Algorithmic Timeline
Live content and engagement tools expanded, and Twitter made its most controversial change by switching to an algorithmic feed.
- Mar 2015: Acquired Periscope for live video streaming.
- Oct 2015: Introduced Twitter Polls and Moments.
- Mar 2016: Switched from chronological to algorithmic timeline.
2017–2020: Profitability and Format Experiments
Twitter finally turned a profit and increased tweet length. It also tested new formats like Fleets, which mimicked Stories from other social platforms.
- 2017: Became profitable; tweet limit increased to 280 characters.
- 2019: Changed reporting metric to monetizable daily active users (mDAU).
- Nov 2020: Launched Fleets (discontinued in August 2021).
2021–2022: Audio, Leadership Changes, and Elon Musk
Twitter introduced audio chat via Spaces, saw a leadership shift, and was thrust into headlines with Elon Musk’s acquisition offer and legal battle.
- May 2021: Spaces launched for live audio rooms.
- Nov 2021: Jack Dorsey resigned; Parag Agrawal became CEO.
- April 2022: Elon Musk offered $44 billion to buy Twitter.
- July–Sept 2022: Musk attempted to back out; Twitter sued and shareholders voted to accept the offer.
Twitter’s Logo Evolution
The Twitter logo has undergone several transformations, moving from a simple wordmark to the iconic bird that defines the brand today.

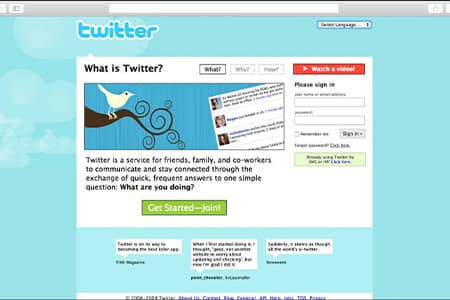
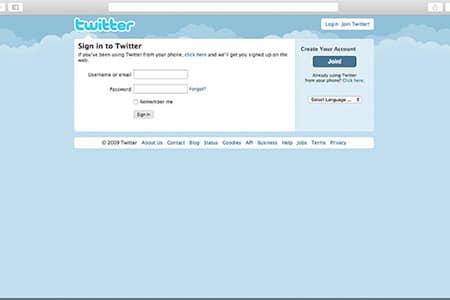
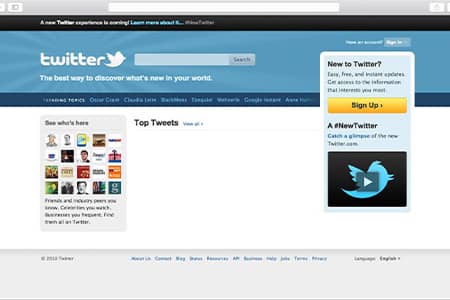
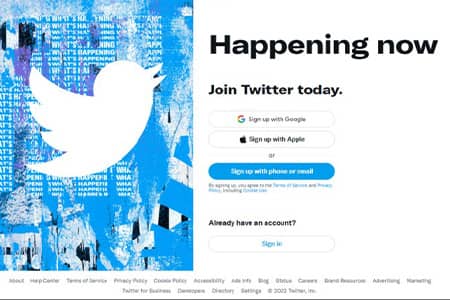
Twitter Homepage Design Over the Years
Here’s how Twitter’s homepage has evolved visually, from its early minimalist design to a modern hub showcasing trending topics and media.
2006–2010
2011–2022
2022–2024: The X Rebrand and Musk Era
After acquiring Twitter in late 2022, Elon Musk launched a sweeping transformation of the platform—from mass layoffs to the radical rebranding of Twitter as “X.”
- Oct 2022: Elon Musk finalizes the $44B acquisition and becomes CEO of Twitter.
- Nov 2022: Twitter lays off around 50% of its global workforce.
- Dec 2022: Banned accounts reinstated; several journalists temporarily suspended.
- Jan 2023: Paid verification relaunches under the new Twitter Blue subscription.
- July 2023: Twitter rebrands to X; blue bird logo retired and replaced with a minimalist X icon.
- 2024: X introduces AI chatbot Grok, expands video features, and tests in-app payments to become an “everything app.”
The Future of Twitter
Under Elon Musk’s leadership, Twitter is undergoing one of the most radical changes in its history. With features in flux and a reimagined business model, what Twitter will look like in 2030 remains anyone’s guess—but its influence is here to stay.
The Future of X (Formerly Twitter)
Under Elon Musk’s ownership, Twitter has been reimagined as X—an all-in-one platform for content, payments, and AI. With features like live video, monetized posts, and the Grok AI chatbot, X is rapidly evolving beyond its microblogging roots. By 2030, the platform may look entirely different, but its cultural impact will likely endure.
FAQs About Twitter’s History
When was Twitter created?
Twitter was created in March 2006 and launched publicly in July of the same year.
Who founded Twitter?
Twitter was founded by Jack Dorsey, Biz Stone, Evan Williams, and Noah Glass.
When did Twitter go public?
Twitter filed for IPO in September 2013 and raised $1.8 billion in November 2013.
Why did Elon Musk buy Twitter?
Elon Musk stated his goal was to restore free speech and unlock Twitter’s potential. The deal closed in 2022 after legal back-and-forth.
What was Twitter’s first tweet?
Jack Dorsey posted the first tweet on March 21, 2006: “just setting up my twttr.”
What happened to Fleets?
Fleets were Twitter’s version of disappearing stories. They launched in 2020 but were shut down in August 2021 due to low engagement.
Why did Twitter change its name to X?
Elon Musk rebranded Twitter as X in July 2023, aiming to transform it into a super app with social, financial, and AI features—all under one platform.
What is Grok on X?
Grok is an AI chatbot integrated into X (formerly Twitter), designed to answer questions and provide commentary, similar to ChatGPT but with a more sarcastic tone.



